
USER GUIDE
Updated 8.2023

2
TX-KEA User Guide
Texas School Ready Project
Children’s Learning Institute at UTHealth Houston
7000 Fannin Street, Suite 2300 | Houston, TX 77030
childrenslearninginstitute.org | texasschoolready.org | cliengage.org
Find us on …
@ChildrensLearningInstitute
@cliengage
The contents of this resource were developed under a grant from the Department of Education. However, those contents
do not necessarily represent the policy of the Department of Education, and you should not assume endorsement by the
Federal Government. (Authority: 20 U.S.C. 1221e-3 and 3474) [45 FR 22497, Apr. 3, 1980. Redesignated at 45 FR 77368,
Nov. 21, 1980, as amended at 45 FR 86297, Dec. 30, 1980]. Portions of the research reported here were supported by the
Institute of Education Sciences, U.S. Department of Education’s through grant R305A110549 to the University of Texas
Health Science Center at Houston. The opinions expressed herein are those of the authors and do not represent views of
the U.S. Department of Education.
3
© 2023 The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston. All Rights Reserved.
TX-KEA User Guide
Table of Contents
About TX-KEA.................................................................................................................................................4
Accessing the TX-KEA Assessment on CLI Engage ..........................................................................................6
Administering TX-KEA ................................................................................................................................... 11
English Subtest Administration Times .................................................................................................... 14
Spanish Subtest Administration Times .................................................................................................... 15
Literacy Screener .......................................................................................................................................... 16
Dyslexia Screener .......................................................................................................................................... 16
Language Domain ..........................................................................................................................................17
Vocabulary Subtest ..................................................................................................................................17
Listening Comprehension Subtest .......................................................................................................... 18
Literacy Domain ............................................................................................................................................ 20
Letter Names Subtest .............................................................................................................................. 20
Decoding Subtest .................................................................................................................................... 21
Letter Sounds Subtest .............................................................................................................................22
Blending Sounds Subtests ....................................................................................................................... 23
Spelling Subtest ...................................................................................................................................... 25
STEM Domain ..............................................................................................................................................26
Mathematics Subtest ..............................................................................................................................26
Science & Engineering Subtest ...............................................................................................................28
Social Emotional Skill Domain ......................................................................................................................29
Social and Emotional Competence Subtest .............................................................................................29
Emotion Management Subtest ................................................................................................................ 30
Executive Functioning Domain ......................................................................................................................31
Working Memory Subtest ....................................................................................................................... 32
Inhibition Subtest ................................................................................................................................... 32
Attention Subtest .................................................................................................................................... 33
Academic Motor Skills Domain ..................................................................................................................... 34
Academic Motor Skills Subtest ............................................................................................................... 34
Language of Administration .......................................................................................................................... 36
Assessing Students with Disabilities .............................................................................................................. 37
FAQs .............................................................................................................................................................40
Please note, resources linked in this user guide may still be in the process of being translated to Spanish
4
© 2023 The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston. All Rights Reserved.
TX-KEA User Guide
About TX-KEA
The Texas Kindergarten Entry Assessment System (TX-KEA) is a collaborative eort between the U.S.
Department of Education, the Texas Education Agency, and the Children’s Learning Institute (CLI) at The
University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston (UTHealth Houston).
TX-KEA is a comprehensive assessment that can be used to evaluate many learning domains critical for
academic success at kindergarten entry and throughout the kindergarten year.
The Language and Literacy domains consist of vocabulary, letter names, and spelling. This serves as the
TX-KEA Literacy Screener and is only administered at the beginning of the school year. These domains also
include listening comprehension, letter sounds, blending, and decoding. The STEM domain consists of
mathematics, science, and engineering. The Motor Skills domain includes fine and visual motor skills. The
Social Emotional domain assesses students’ social emotional competence and emotion management. The
Executive Functioning domain assesses students’ inhibition, working memory, and attention.
TX-KEA is a comprehensive assessment; however, you have the flexibility to administer whichever subtests
that you and your administrators are most interested in. You also have the flexibility to administer these
subtests in any order.
KINDERGARTEN PROGRESS MONITORING
In Fall 2017, CLI received a grant from the Brown Foundation to expand TX-KEA into a kindergarten progress
monitoring tool. The kindergarten entry screener serves as the BOY (beginning-of-year) assessment for this
progress monitoring tool; the MOY (middle-of-year) and EOY (end-of-year) assessments and reports were
developed and validated during the 2017-18 school year in Texas classrooms.
PILOT ITEMS
As part of CLI’s ongoing eorts to evaluate the performance of TX-KEA, additional items may be piloted and
included in some measures during the school year. These items will be identified for teachers as a “pilot item”
and are not included in the student’s score.
5
© 2023 The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston. All Rights Reserved.
TX-KEA User Guide
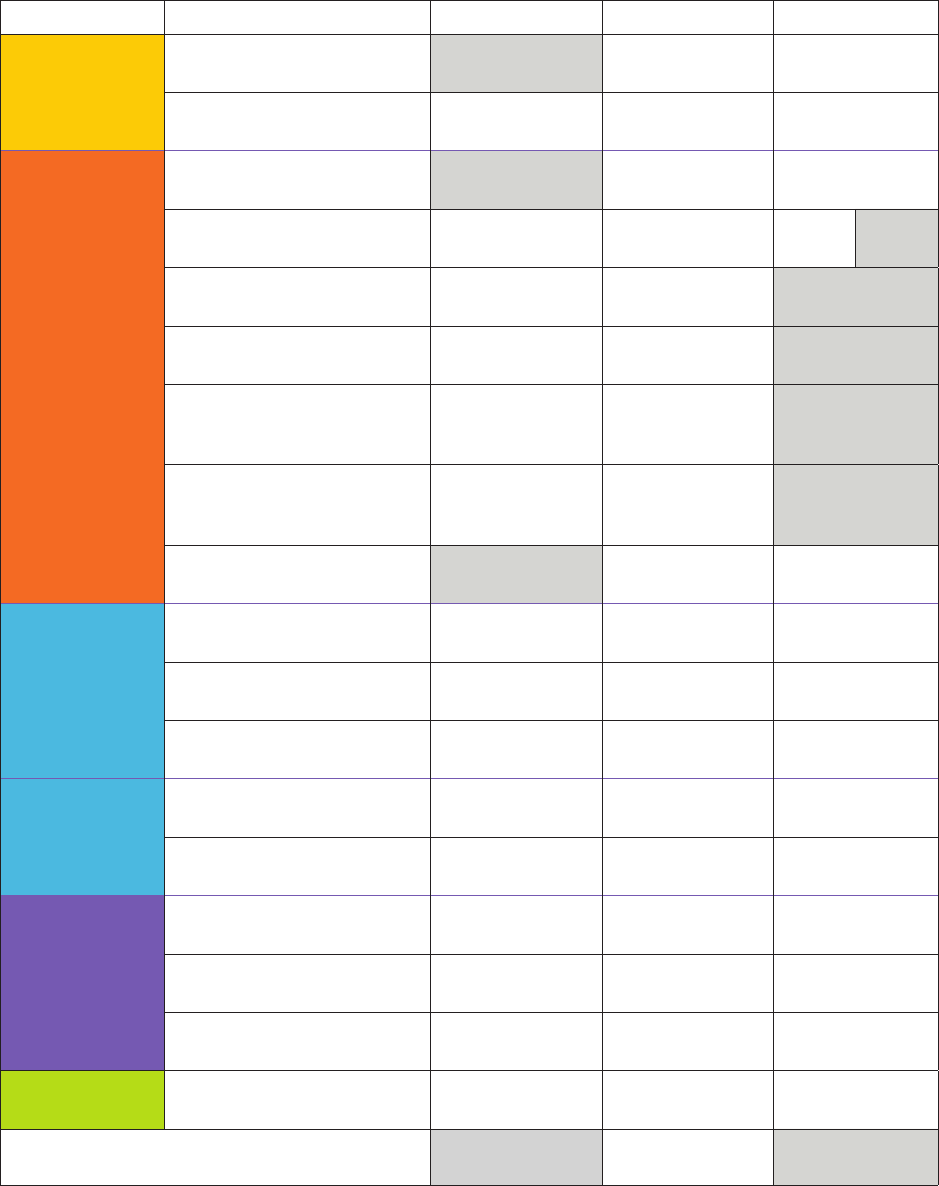
TXKEA DOMAINS AND SUBTESTS ENGLISH AND SPANISH
DOMAIN MEASURE BOY (Wave 1) MOY (Wave 2) EOY (Wave 3)
LANGUAGE
Vocabulary
Vocabulario
En, Sp En, Sp En, Sp
Listening Comprehension
Comprensión Auditiva
En, Sp En, Sp
LITERACY
Letter Names
Nombres de las Letras
En, Sp En, Sp En, Sp
Decoding
Decodificación
En, Sp En, Sp En Sp
Letter Sounds-Receptive
Sonidos de las Letras-Receptivo
En, Sp En, Sp En, Sp
Letter Sounds-Expressive
Sonidos de las Letras-Expresivo
En En
Blending-Receptive
Combinación de Sonidos-
Receptivo
En, Sp En En, Sp
Blending-Expressive
Combinación de Sonidos-
Expresivo
Sp En, Sp
Spelling
Ortografía
En, Sp En, Sp En, Sp
STEM
Math, Part 1
Matemáticas, Parte 1
En, Sp En, Sp En, Sp
Math, Part 2
Matemáticas, Parte 2
En, Sp En, Sp En, Sp
Science
Ciencias
En, Sp En, Sp En, Sp
SOCIAL
EMOTIONAL
Social and Emotional Competence
Socioemocional
En, Sp En, Sp En, Sp
Emotion Management
Manejo de Emociones
En, Sp
EXECUTIVE
FUNCTION
Working Memory
Memoria
En, Sp
Inhibition
Inhibición
En, Sp
Attention
Atención
En, Sp
ACADEMIC
MOTOR SKILLS
Academic Motor Skills
Motricidad Académica
En, Sp
Literacy Screener
(BOY)
Dyslexia Screener
(EOY)

6
© 2023 The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston. All Rights Reserved.
TX-KEA User Guide
GETTING READY
Visit the TX-KEA Toolkit under the Training & Support tab to download TX-KEA resources, including:
• TX-KEA User Guide
• TX-KEA Scoring Guidelines
• TX-KEA Reporting How-To-Guides
• TX-KEA Parent Feedback Forms
Accessing the TX-KEA Assessment on
CLI Engage
TX-KEA is available on the CLI Engage. To access TX-KEA, teachers, administrators, and district personnel will
need to log in to cliengage.org using any of the following sign in options: Google, ClassLink, Clever, Okta, or
Microsoft account. If you are new to CLI Engage this year, you must have completed the registration process by
clicking the link in the registration email before attempting to log in.
LOGGING IN TO CLI ENGAGE
• You will need a desktop computer, laptop, or tablet with Internet access. Open a new browser
window and go to cliengage.org.
• Click “LOGIN” on the top right corner of the screen.
• On the next screen, select your login option: Google, ClassLink, Clever, Okta, or Microsoft
• Enter your username and password and click “Sign in.”
GOOGLE ACCOUNT SETUP APPLICABLE FOR MOST USERS:
If you do not have a Google Account, you can create one using your existing email account or by creating
a Gmail account at the following link: accounts.google.com/signup
To use your current email address to set up a new Google Account, click “I prefer to use my current
email address” below the “Choose Your Username” box. Please write down your username and password
somewhere convenient.
CLI ENGAGE DASHBOARD
After logging in, you will see a dashboard that includes links to:
• SCREENING, PROGRESS MONITORING, & OBSERVATION tools, including the TX-KEA and
Assessment Practice Area
• ONLINE LEARNING AND PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT for access to online courses
• ACTIVITIES & MATERIALS for teachers and families (CIRCLE Activity Collections)
• QUALITY IMPROVEMENT & INNOVATION to access collaborative tools
7
© 2023 The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston. All Rights Reserved.
TX-KEA User Guide
• ADMINISTRATIVE TOOLS to manage your student roster and classes
SUBMIT A HELP TICKET IF YOU NEED ASSISTANCE.
The help ticket button is always available at the top of the screen,
in the website navigation. A CLI sta member will respond back
through email.
TO PRACTICE TXKEA:
1. Login to cliengage.org.
2. Click the “Assessment Practice Area” button under the red “Screening, Observation, and Assessment”
tab.
3. On the next screen, click the “Texas Kindergarten Entry Assessment” button.
4. Now you will see a class of demo children. Be sure to select the correct wave in the top-right corner
to view subtests.
5. In the assessment practice area you can:
− Practice assessing children
− View assessment items in each subtest
− Practice pulling class-level reports
TO ACCESS TXKEA:
1. Login to cliengage.org.
2. Click the “Texas Kindergarten Entry Assessment” button under the red “Screening, Observation, and
Assessment” tab.
3. On the “Class List” page, click on the name of the class that includes the students you wish to assess.
Be sure to select the correct wave.
4. Next, you will see the “Student View” page. This page allows you to:
− Choose to administer an assessment in English or Spanish.
− See the benchmark scores for students in a class.
− Launch an assessment, multiple assessments, or a subtest.
− Assess oine.
− View class-level reports, including small group and parent reports.

8
© 2023 The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston. All Rights Reserved.
TX-KEA User Guide
STUDENT VIEW PAGE
OFFLINE ASSESSMENT
The oine assessment feature can be used to assess students when an internet connection is not available at
the time of administration. The oine assessment can also be used in the CLI Engage assessment practice
area.
Note: An internet connection is required for the initial setup.
This feature downloads the assessment for your class in only one language, English or Spanish. If you need
to assess in both languages, you need to complete the process below in one language (downloading the
assessment, assessing oine, uploading results) and then repeat in the other language.
You can view the instructions for the oine assessment in our TX-KEA Oine Assessment how-to guide.
EXCLUDING AND HIDING MEASURES
The green button with a white circle indicated in the screenshot above is used to “exclude” a student OR the
entire class from a specific measure or sub-task. The completion report takes this exclusion into account when
tabulating completion rates. For example, in a class of 10 students, if 2 are excluded and the remaining 8 are
tested, the completion report will indicate 100%. If the students are not formally excluded using this feature,
the report would indicate an 80% completion rate. Anyone with access to a class can exclude measures.
If all students are excluded from a measure (i.e., the measure is not being administered to any student),
it is more ecient to use the “Exclude All” button that appears just below the measure name, rather than
excluding each individual child. This feature excludes the entire class from a measure or
sub-measure with one click. In this case, the “Launch” icon is replaced by a gray square
preventing the measure from being administered to the student. This can also be done by an administrator,
but would have to be set for every class (i.e., it cannot be performed school-wide). In this case, the teacher
would not see the measures that had been excluded by the administrator.
If a teacher excludes all students from a measure, it is helpful to also remove it from view using the “Hide/
TX-KEA Subtests
Launch Multiple
Subtests
Launch Single
Subtest
Exclude Task

9
© 2023 The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston. All Rights Reserved.
TX-KEA User Guide
Display Measures” feature. This makes it easier to locate measures you are actually assessing without having
to scroll through the full list of available measures. It is important to note that the “Hide/Display Measures”
button hides a measure from view for navigational purposes only. Hiding a measure does not aect data or
reporting. Hiding is set by each user, and the system remembers the user’s preference; therefore no user can
hide measures for another user.
MANAGING CLASS ROSTERS
There are several options for uploading data into CLI Engage to create accounts for teachers and other sta, as
well as adding children into the system for progress monitoring. You can view the instructions for uploading
teacher and student data on our Uploading Data web page.
TXKEA REPORTS ON CLI ENGAGE
TX-KEA provides you with several dierent reports. The reports can be completed at the class, campus, and
district levels.
• Completion Report: tracks completion of selected assessments.
• Class Summary Report: allows teachers to view performance of all children in every subject area by
classroom.
• Custom Score Report: allows access to a separate report for the TX-KEA Literacy Screener which is
only administered at BOY.
• Class Summary (Percentile Rank) Report: translates raw scores for each subtest and converts them
to percentiles. Then you are able to see how a student scores between the 1st to the 99th percentile
making it easier to compare scores where the score varies across each measure. It’s a dierent scale
that is available to help you analyze your data.
• Growth Report: allows teachers to view their children’s growth over time, throughout the school year,
comparing each assessment window.
• Student Report for Teachers: allows teachers to view children’s performance across all subject areas
per student.
• Student Report for Parents: connects families to activities that enable them to support their children
at home. Teachers can communicate students’ strengths and areas needed for growth.
• Group Report: groups children with scores below age-related benchmarks and recommends activities
for further skill development.
10
© 2023 The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston. All Rights Reserved.
TX-KEA User Guide
HOWTO DOCUMENTS
Several how-to guides can be viewed on our How-To Guides webpage.
FAMILY ENGAGEMENT
Engaging families in student’s education is a vital component to building strong relationships between
school and home. This provides opportunities to support skill development throughout the day. CLI Engage
oers many tools and resources to support family and parent engagement, including free family activities,
a customized parent report of child progress monitoring results, and free resources for hosting family
engagement sessions.
CLI has developed a family engagement toolkit and online professional development, available on CLI Engage
at no cost. View our Family Engagement Resources web pages on CLI Engage to learn more and download
resources.
Sharing Data with Families
Teachers using TX-KEA can share student scores with families electronically, via a QR code. Teachers can
also send families activities that are designed to support skill development at home. Electronic parent reports
provide:
• Performance categories at a glance (see right)

11
© 2023 The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston. All Rights Reserved.
TX-KEA User Guide
• Family resources that are linked through a QR code (see right)
Including Families in the Assessment Process
Families are valuable sources of information on student’s skill development.
The Parent Feedback forms align with the learning domains of TX-KEA and
can be used in their portfolios and at parent-teacher conferences to provide
a full picture of their development. The Parent Feedback Forms can be
accessed from the CLI Engage dashboard.
CIRCLE Activity Collection for Families
Many studies have shown that families and teachers working together to
support children’s development can lead to better outcomes for children.
This collection includes fun, easy activity ideas that families can do together to help support important school
readiness skills for children ages 0-6. You can view the collection on our CLI Engage Family website.
Teachers can also share family activities directly with families via email throughout the school year. This
feature is accessed through the small group report for TX-KEA. After uploading parent email addresses,
teachers can select and share activities aligned to each child’s areas for skill development, so children are
supported at school and home. You can view more on our Create My Activities in the CIRCLE Activity
Collection how-to guide.
Administering TX-KEA
TESTING MATERIALS
Devices for Administration
• Computer/laptop with Windows operating system.
• Tablet screen size must be larger than 8" x 5" (iPads not recommended for use because of known audio
issues)
• Headphones
Other Materials
• Pencils and erasers for the Spelling subtest
• TX-KEA Scoring Guidelines - printed
GENERAL TESTING GUIDELINES
• TX-KEA is intended to be administered by the classroom teacher.
• Note that students will vary in terms of their familiarity and comfort with assessments.
• Print this User Guide in advance. Keep it with you so that you can refer to each subtest section
throughout administration.

12
© 2023 The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston. All Rights Reserved.
TX-KEA User Guide
• Be suciently familiar with the CLI Engage platform.
• Make sure all equipment is working properly.
• Have a plan for managing your class while you work with one student.
• You do not need to complete TX-KEA in one sitting, but should complete a subtest in one sitting.
• Remember to be consistent and accurate when administering TX-KEA.
ASSESSMENT WINDOW
School districts and charter schools set their own assessment windows on CLI Engage. For the kindergarten
entry screener, the TX-KEA development team recommends an assessment window beginning in September
and ending in October, but the assessment will be available beyond this recommended window on CLI
Engage. Schools may slightly adjust this window based on their particular needs and schedules for all three
progress monitoring waves.
4 RESPONSE TYPES
Student-Selected Response Items
How should the teacher and student situate themselves?
• You can sit side-by-side.
• You can sit adjacent to each other.
How do you administer?
• Student must wear headphones.
• Have student listen to the audio prompt and make a selection.
• You do not prompt student.
How is it scored?
• Program scores each item.
Teacher-Recorded Response Items
How should the teacher and student situate themselves?
• You can sit side-by-side.
• You can sit adjacent to each other.
How do you administer?
• Student must wear headphones.
• Prompts will either be audio prompts given by the test or teacher prompts
read from the screen.

13
© 2023 The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston. All Rights Reserved.
TX-KEA User Guide
• Have student listen to the audio prompt or your teacher prompt and verbalize
their response.
How is it scored?
• Program scores each item.
• For some teacher-recorded response items, the teacher will indicate whether the student response was
correct or incorrect by clicking a colored button.
− Incorrect student response: blue button, or press the left arrow on the keyboard
− Correct student response: Click the purple button or press the right arrow on the keyboard.
“Right is right!”
Teacher-Reported Behavior Checklists
How do you administer?
• Complete electronically in CLI Engage.
• Reflect on student’s typical interactions.
• Answer all questions.
• Only complete Checklists for 5 students or less in one sitting.
How is it scored?
• Program scores each checklist.
Student-Written Response Items (Specific to Spelling Subtest)
How do you administer?
• Teacher will prompt students to write words.
• Students will write responses on a sheet of paper.
How is it scored?
• Teacher will score on CLI Engage.
14
© 2023 The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston. All Rights Reserved.
TX-KEA User Guide
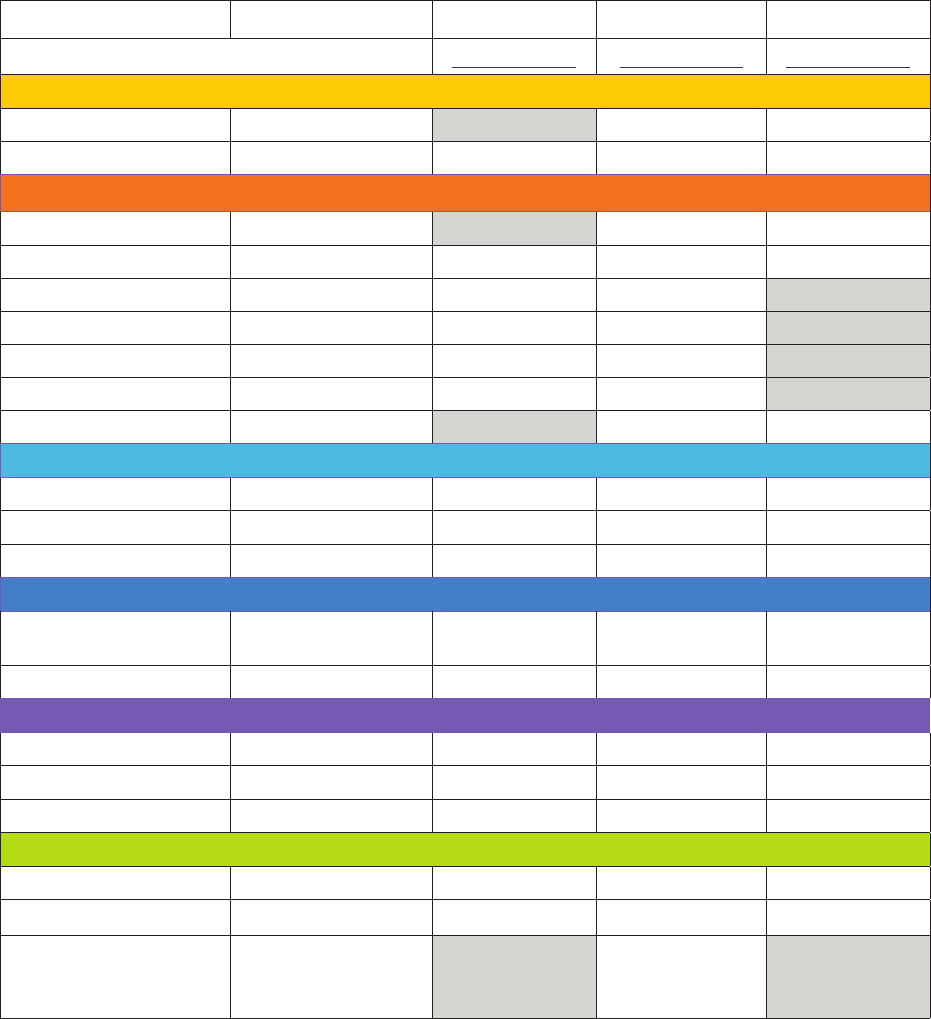
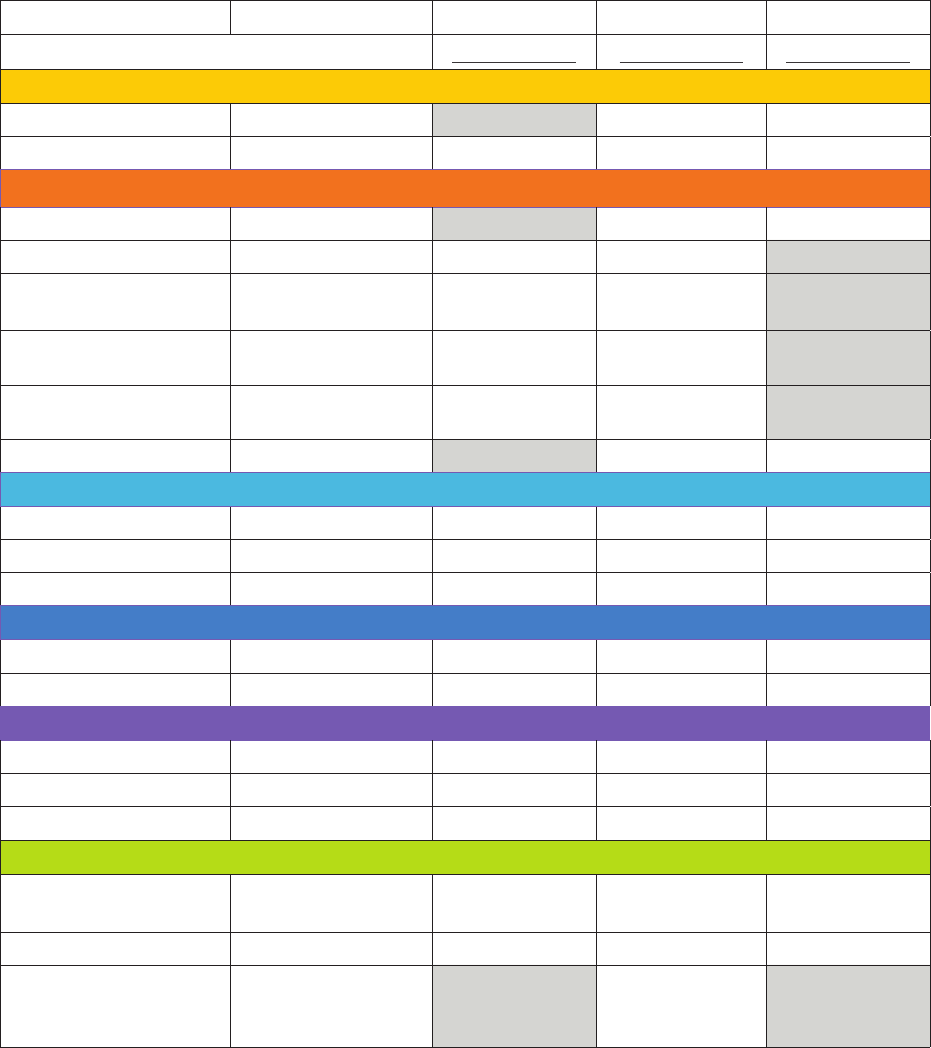
ENGLISH SUBTEST ADMINISTRATION TIMES
MEASURE RESPONSE TYPE BOY (Wave 1) MOY (Wave 2) EOY (Wave 3)
Time In Minutes Time In Minutes Time In Minutes
LANGUAGE
Vocabulary
Teacher-recorded 1 2 1
Listening Comprehension
Student-selected 3 5
LITERACY
Letter Names Teacher-recorded
1 1 1
Decoding Teacher-recorded
1-2 2-3 1-2
Letter Sounds-Receptive Student-selected
1-2 1-2 1-2
Letter Sounds-Expressive Teacher-recorded
1-2 1-2
Blending-Receptive Student-selected
5 2 1
Blending-Expressive Teacher-recorded
2
Spelling Student-written
5 5 5
STEM
Math, Part 1 Teacher-recorded
4-5 1-2 3-4
Math, Part 2 Student-selected
4-5 1-2 3-4
Science Student-selected
5 5 5
SOCIAL EMOTIONAL
Social Emotional
Competence
Behavior Checklist 2-3 3 3
Emotion Management
Behavior Checklist 2-3
EXECUTIVE FUNCTION
Working Memory Student-selected
2-3
Inhibition Student-selected
2-3
Attention Student-selected
2
ACADEMIC MOTOR SKILLS
Academic Motor
Behavior Checklist 3
Total Time
43-51 24-29 33-38
Total Time
Literacy and Dyslexia
Screeners
Literacy Screener
(BOY) 5-7 mins
Dyslexia Screener
(EOY) 5-9 mins
Additional measures may be added during the school year.
15
© 2023 The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston. All Rights Reserved.
TX-KEA User Guide
SPANISH SUBTEST ADMINISTRATION TIMES
MEASURE RESPONSE TYPE BOY (Wave 1) MOY (Wave 2) EOY (Wave 3)
Time In Minutes Time In Minutes Time In Minutes
LANGUAGE
Vocabulario
Teacher-recorded 1 2 1
Comprensión Auditiva
Student-selected 5 5
LITERACY
Nombres de las Letras Student-selected
1 1 1
Decodificación Teacher-recorded
1-2 1-2 1-2
Sonidos de las Letras-
Receptivo
Student-selected
1-2 1-2 1-2
Combinación de Sonidos-
Receptivo
Student-selected
4 4
Combinación de Sonidos-
Expresivo
Teacher-recorded
2 2
Ortografía Student-written
5 5 5
STEM
Matemáticas, Parte 1 Teacher-recorded
4-5 1-2 3-4
Matemáticas, Parte 2 Student-selected
4-5 1-2 3-4
Ciencias Student-selected
5 5 5
SOCIAL EMOTIONAL
Socioemocional
Behavior Checklist 2-3 3 3
Manejo de Emociones
Behavior Checklist 2-3
EXECUTIVE FUNCTION
Memoria Student-selected
2-3
Inhibición Student-selected
2-3
Atención Student-selected
2
ACADEMIC MOTOR SKILLS
Motricidad Académica
Behavior Checklist 3
Total Time
44-52 22-26 34-38
Total time
Literacy and Dyslexia
Screeners
Literacy Screener
(BOY) 5-7 mins
Dyslexia Screener
(EOY) 8-12 mins
Additional measures may be added during the school year.

16
© 2023 The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston. All Rights Reserved.
TX-KEA User Guide
LITERACY SCREENER
The state-mandated the TX-KEA Literacy Screener is available as a brief assessment of language, literacy, and
emergent writing.
The literacy screener is a part of the BOY measures oered in TX-KEA. The screener takes 5-7 minutes to
administer and includes a mix of one-on-one and small group administrations. It oers screening to evaluate
Emergent Literacy (Letter names), Emergent Writing (Spelling), and Language (Vocabulary).
The TX-KEA Literacy Screener is comprised of the Vocabulary, Letter Names, and Spelling subtests. Students
will score within the “on track” (green), “monitor” (yellow) or “support” (red) benchmarks ranges for each
subtest. These scores assist districts in informing student instruction. The composite score produced can be
used to identify students who meet the “support” benchmark because they are in the bottom 25th percentile.
The Statewide Kindergarten Readiness score is comprised of the Vocabulary, Letter Names, and Spelling
subtests. Students must meet the “on track” (green) benchmark for all three subtests to meet the kindergarten
readiness criteria determined by TEA. Districts can use the additional subtest data to make individual
determinations regarding students who may require additional support.
For more information regarding assessment in PK-2nd grade, please visit TEA’s Data Driven Instruction in
Early Childhood Education website or contact TEA: ECE Support Portal.
DYSLEXIA SCREENER
The TX-KEA dyslexia screener found in wave 3 (EOY) is comprised of “Letter Sounds (receptive and
expressive), Blending Sounds (receptive and expressive) in English and Sonidos de las Letras (receptivo),
Combinación de Sonidos (receptivo y expresivo) and Decodificación in Spanish.
CLI Engage automatically calculates when you complete all of the required measures which are sequenced
in the same color in Wave 3 (EOY) as seen below. If a student’s score shows up red, there may be reading
Dyslexia
Screener Subtests
in Blue
Dyslexia
Screener Results
Select Wave 3
DRC
Results

17
© 2023 The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston. All Rights Reserved.
TX-KEA User Guide
diculties you need to consider.
The Dyslexia Referral Checklist (DRC) evaluates areas considered to be important for early reading (e.g.,
language-based skills, letter and letter-sound knowledge, phonological awareness, phonemic awareness,
decoding, and spelling).
We strongly recommend that the DRC be used to incorporate observations. The DRC has a point scale once
tallied that will indicate whether the student may be at risk. A score of 24 or greater indicates possible further
evaluation. CLI Engage automatically calculates the scoring and provides the total score in red if the student is
at risk.
Download the Kindergarten DRC manual (English and Spanish) to use with TX-KEA dyslexia screener and log
in to CLI Engage to complete the dyslexia screener and the checklist.
LANGUAGE DOMAIN
Vocabulary Subtest (Vocabulario)
Vocabulary is a foundational language skill that supports learning in all content domains. Knowing a student’s
vocabulary abilities helps teachers adjust their own vocabulary usage during instruction to levels that are most
beneficial for individual students. This subtest is available in English and Spanish.
FEATURES OF THIS SUBTEST
• Untimed
• Teacher-recorded responses
• Picture naming task
DIRECTIONS
Directions will be provided on the screen after the teacher enters the subtest.
1. Headphones are not worn by the student.
2. Silently review the general administration directions on the screen in black font.
3. A picture will appear for the student.
4. The prompt you will say to the student is shown on the screen in colored font. Read the entire
prompt.
5. After the student provides a verbal response, select the purple button for a correct response and blue
button for an incorrect response.

18
© 2023 The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston. All Rights Reserved.
TX-KEA User Guide
6. Use the Vocabulary Scoring Guidelines for list of correct responses.
7. The computer will score the response.
ALLOWABLE QUERIES/PROMPTS FOR VOCABULARY SUBTEST
There may be occasions when a student provides a response that requires the teacher to follow up with a
query, or prompt, rather than immediately scoring the response. There are four follow-up queries that can be
used. Each of these four prompts can only be used once per test item. If the same prompt would be needed a
second time on a given item, then the prompt should not be repeated and the item should simply be scored
as incorrect. More than one type of prompt can be used on the same test item if absolutely necessary, but
this would be very rare. If the student’s response to a prompt does not require an additional prompt (as will
usually be the case), then score the student’s response as correct or incorrect using the Vocabulary Scoresheet.
Prompts should not be used to give students a second chance to get the answer right. Most initial responses
can be immediately scored. Prompts should only be used under the following circumstances:
• If student responds in the wrong language:
− “What’s the English word?” or “¿Cual es la palabra en Español?”
• If student labels the wrong part of a picture:
− “What is this (point)?” or “¿Que es esto (point)?”
• If student’s response reflects a higher level of categorization (e.g., student responds “animal” for dog)
− “What kind?” or “¿Que tipo?”
• If student’s response reflects a lower level of categorization (e.g., student responds “golden retriever”
for dog)
− “Tell me another word.” or “Dime otra palabra.”
Listening Comprehension Subtest
(Comprensión Auditiva)
Listening comprehension is a foundational language skill that supports learning in all content areas. TX-KEA
assesses the student’s ability to understand verbal information and follow directions. Knowing your student’s
receptive language abilities will allow you to adjust the complexity of your own language during instruction.
This will help your students understand your instruction, and it will help you scaold their language
development. This subtest is available in English and Spanish.

19
© 2023 The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston. All Rights Reserved.
TX-KEA User Guide
FEATURES OF THIS SUBTEST
• Untimed
• Single-select items and multiple-select items
DIRECTIONS
Directions will be provided on the screen after the teacher enters the subtest
1. Headphones are worn by the student.
2. Silently review the administration directions on the screen.
3. The student is told what to do through the headphones.
4. Grayed pictures will appear on the screen while the computer provides auditory instructions.
5. Once the computer is finished providing auditory instructions, the pictures will change to color,
which allows the student to select the picture(s) that best illustrates the sentence they just heard.
Items are a combination of single-select (one answer) and multiple-select (more than one answer).
Note: Even though this is a self-guided test, teachers should watch students as they proceed to make sure
they are waiting for pictures to change from gray scale to color before making selections.
ALLOWABLE PROMPTS FOR LISTENING COMPREHENSION SUBTEST
• If the student does not respond by pointing to a picture(s) within 5 seconds:
− “Go ahead. Point to the picture(s).”
• If the student points to a picture before it changes from gray scale to color:
− “Wait until the computer is done talking.”
− “Wait until all the pictures turn to color.”
Failure of the student to respond after an extended period of time will result in the item being scored as
incorrect, and the program will advance to the next test item.

20
© 2023 The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston. All Rights Reserved.
TX-KEA User Guide
LITERACY DOMAIN
Letter Names Subtest (Nombres de las
Letras)
The Letter Names subtest assesses students’ knowledge of the names associated with various letters of the
alphabet. Letter names is one component of letter knowledge which is an excellent predictor of reading
achievement. This subset is available in English and Spanish.
FEATURES OF THIS SUBTEST
• Untimed
• Teacher-recorded responses for English
administration
• Student-selected responses for Spanish
administration
DIRECTIONS
Directions will be provided on the screen after the teacher enters the subtest.
English:
1. Headphones are not worn by the student.
2. A letter will appear on the screen for the student.
3. The prompt you will say to the student is shown on the screen in colored font. Read the entire
prompt.
4. The student responds verbally.
5. Score the student’s verbal response by selecting the appropriate button on the screen. (Correct =
purple button / Incorrect = blue button)
Spanish:
1. Headphones are worn by the student.
2. Four letters appear on the screen while the computer provides auditory instructions.
3. The student selects the best response.
4. The computer will score the response.

21
© 2023 The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston. All Rights Reserved.
TX-KEA User Guide
ALLOWABLE PROMPTS FOR LETTER NAME SUBTEST
Spanish Letter Names:
• If the student does not respond by pointing to a letter within 5 seconds:
− “Señala la letra.”
English Letter Names:
For the English test of Letter Names, allow 5 seconds for the student to respond before providing a prompt,
“Go ahead. Take a guess. What letter is this?” The student can be prompted only once during the test. If
the student does not reply with the correct answer within 10 seconds after the one follow-up statement is
provided, then the item is scored as incorrect.
• If student responds with the letter sound instead of the letter name:
− “That’s the sound this letter makes. Tell me the name of this letter.”
• If student responds with a word that starts with the letter:
− “Tell me the name of this letter.”
• If student responds in the wrong language:
− “What’s the English letter?”
• If student responds with the Spanish name for the letter, e.g., Bay instead of Bee.
− “Tell me the English name.”
Decoding Subtest (Decodificación)
The Decoding subtest measures ability to read non-high frequency words by sounding them out (decoding)
rather than knowing the whole word from memory (rote visual memory).
FEATURES OF THIS SUBTEST
• Untimed
• Teacher-recorded responses
DIRECTIONS
The teacher and student should sit side-by-side. The student should read the words and the teacher will
score the response as correct or incorrect.
Say: “I am going to show you some words and I would like you to try to read them to me. What word is

22
© 2023 The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston. All Rights Reserved.
TX-KEA User Guide
this?” The student responds: “hot.”
After the first item, the instructions can be shortened to: “What word is this?”
If the child sounds out words, letter by letter, e.g., /h/ /o/ /t/, prompt by saying: “Now say the word
smoothly.” This prompt can be used each time the child attempts to read the word by sounding out each
letter.
Only give credit if the child is able to read the word smoothly and accurately. If the child does not
respond in 5-10 seconds, feel free to encourage the child to guess. If after 10 seconds the child does not
respond, record incorrect and proceed with the rest of the subtest.
Letter Sounds Subtests (Sonidos de las
Letras)
There are two letter sounds subtests that assesses students’ knowledge of letter sounds—Letter Sounds-
Receptive and Letter Sounds-Expressive. For an understanding of a student’s early literacy development that
is most complete and useful for instructional planning, we encourage educators to assess both letter names
and letter sounds. Letter knowledge at kindergarten entry is a strong predictor of literacy achievement. This
subtest is available in English and Spanish.
FEATURES OF THIS SUBTEST
Teachers must complete both Letter Sounds-Receptive and Letter Sounds-Expressive to calculate the student’s
score for the Letter Sounds subtest. In the Letter Sounds-Receptive subtest, a letter’s sound is given and the
student determines the corresponding printed letter. In the Letter Sounds-Expressive subtest, a letter is
shown on the screen and the student gives the corresponding sound.
• Letter Sounds-Receptive includes student-selected
items
• Letter Sounds-Expressive includes teacher-recorded
items
• Untimed
• Student-selected responses and teacher-recorded
responses
LETTER SOUNDSRECEPTIVE DIRECTIONS STUDENTSELECTED
Directions will be provided on the screen after the teacher enters the subtest.
1. Headphones are worn by the student.
2. Four letters appear on the screen for the student to view.
3. The computer provides auditory instructions about which letter to point to.
4. The student selects one of the letters.

23
© 2023 The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston. All Rights Reserved.
TX-KEA User Guide
5. The computer scores the student’s response.
LETTER SOUNDSEXPRESSIVE DIRECTIONS TEACHERRECORDED
This section measures the student’s knowledge of letter sounds. The teacher and student should sit side-
by-side.
Say: “We are going to look at some letters and see if you know the sound they make. It is OK to guess if
you do not know the sounds. Some letters make only one sound and some make more than one sound.
Try to tell me at least one sound the letters make. Ready?”
If the students says the name of the letters, you can say: “Tell me the sound.”
ALLOWABLE PROMPTS FOR LETTER SOUNDS SUBTEST STUDENTSELECTED
• If the student does not respond within 10 seconds.
− Prompt student to point to a letter. If the student does not reply with the correct answer within
10 seconds after the appropriate follow-up statement is provided, then the item is scored as
incorrect. Only use this prompt once during the subtest.
• If the student says “I don’t know” or shrugs shoulders, and does not initiate touching the screen:
− While sweeping pointed finger in a circular motion just above the screen, teacher says, “That’s
OK. Just go ahead and point to one. Point to the letter that makes (sound) .” or “Está bien.
Solamente señala una. Señala la(s) letra(s) que hace(n) (sound) .”
• If the student responds by touching multiple letters.
− Teacher says, “Just point to one letter” or “Solo señala un letra.” Teacher then scores the item as
incorrect by selecting an incorrect letter on the screen. The computer will automatically advance
to the next item.
Blending Sounds Subtests
(Combinación de Sonidos)
There are two blending Sounds subtests that assesses students’ phonological awareness, or sensitivity to the
sound structure of oral language–Blending-Receptive and Blending-Expressive. Phonological awareness is
necessary for learning to read and write and is predictive of literacy achievement. This subtest is available in
English and Spanish.

24
© 2023 The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston. All Rights Reserved.
TX-KEA User Guide
FEATURES OF THIS SUBTEST
• Blending-Receptive includes student-selected items
• Blending-Expressive includes teacher-recorded items
• Untimed
BLENDINGRECEPTIVE DIRECTIONS STUDENTSELECTED
Directions will be provided on the screen after the teacher enters the subtest.
1. Headphones are worn by the student.
2. Three or four grayed images will appear on the screen, one at a time. The pictures are labeled by the
computer as they appear.
3. The computer will provide a series of sounds, and ask student to point to the image of the blended
word.
4. The grayed pictures will change to color, allowing the student to select the picture that illustrates the
word formed by blending the sounds together.
5. The computer will score the response.
BLENDINGEXPRESSIVE DIRECTIONS TEACHERRECORDED
Directions will be provided on the screen after the teacher enters the subtest.
1. Headphones are worn by the student. The student should not be able to see the screen.
2. Teacher will say, “We are going to listen to some sounds and see if you know the word they make. It is
OK to guess if you do not know the word. Ready?”
3. The student will hear the instructions, “Put these sounds together,” then listen to a word split into the
component sounds. The word will not be repeated.
4. The student will say the complete word back to the teacher.
5. The teacher will score whether or not the student correctly identified the word.
ALLOWABLE PROMPTS FOR BLENDING SOUNDS SUBTEST STUDENT
SELECTED
• If the student does not respond within 10 seconds:
− Prompt student to point to a picture. If the student does not reply with the correct answer within 10
seconds, then the item is scored as incorrect. Only use this prompt once during the subtest.
• If the student responds by pointing to multiple images:
− Teacher says, “Just point to one picture” or “Solo señala un dibujo.” Teacher then scores the item

25
© 2023 The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston. All Rights Reserved.
TX-KEA User Guide
as incorrect by selecting an incorrect image on the screen. The computer will automatically
advance to the next item.
• If the student says the word but fails to point:
− Teacher says, “Go ahead and put your finger on ” or “Pon tu dedo en .”
ALLOWABLE PROMPTS FOR BLENDING SOUNDS SUBTEST TEACHER
RECORDED
• Ensure the student says the word fluently.
• If needed, prompt the student: “Now, say it fast.”
Spelling Subtest (Ortografía)
The Spelling subtest assesses students’ early spelling abilities, which is the ability to use sound-symbol
relationships to write words. TX-KEA assesses spelling because it is highly related to later literacy
achievement. Attempting to spell words requires students to apply multiple literacy skills simultaneously,
such as alphabet knowledge and phonological awareness. Dierent items are included on each wave of the
subtest. All materials can be downloaded from the TX-KEA Scoring Guidelines page.
FEATURES OF THIS SUBTEST
• Approximately 7-10 minutes in length
• Untimed
• Student-written responses
• Can be administered individually or in small groups (approximately 5
students)
This subtest requires the following materials that can be downloaded from the TX-KEA Scoring Guidelines:
• Teacher Demonstration Video of a teacher modeling the spelling of a sample word – available on the
direction page after launching the Spelling subtest for any student
− Note: Alternatively, Spelling Model Cards to allow the teacher to demonstrate the task if
technology is unavailable. Use of the video is strongly recommended.
• Student Form – print one for each student
• Teacher script with picture cards –print two-sided
• Scoring Guidelines
• Letter Approximations
DIRECTIONS
Use the teacher script for administration instructions. The teacher script can be downloaded from the
TX-KEA Scoring Guidelines on CLI Engage.

26
© 2023 The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston. All Rights Reserved.
TX-KEA User Guide
ALLOWABLE PROMPTS FOR SPELLING
English:
• If the student does not put their pencil down, but they seem to be done spelling the word or have
paused for 10-15 seconds, then prompt: “Are you done with that word?” Allow student to respond. If
they say no, then allow up to 10-15 seconds before you stop them: “Let’s go on to the next word.”
• If a student does not understand or says “I don’t know,” say: “That’s okay. Just write what you can and
put the pencil down when you’re done.”
• If a student is scribbling but staying within the line, then allow them to “scribble/write” for 10-15
seconds then stop them: “Okay that’s all the time we have for that word so put your pencil down.”
• If a student seems to understand to write on the line, you do not need to remind them to write on the
line after item 1, but if they are writing outside of the line repeat: “Remember to write on the line.”
Spanish:
• Si el alumno no ha bajado su lápiz pero parece haber terminado de escribir o ha pausado por
aproximadamente 10-15 segundos, diga: “¿Terminaste con esa palabra?” Permita que el alumno
responda. Si responde que no, entonces permítale continuar por aproximadamente 10-15 segundos
más antes de dar por terminado el ítem diciendo: “Continuemos con la próxima palabra.”
• Si el alumno no entiende o dice “Yo no sé” diga: “Está bien. Escribe lo que puedas y descansa el lápiz
sobre la mesa cuando hayas terminado.”
• Si el estudiante produce garabatos pero se queda dentro sobre la linea, permitale seguir escribiendo
por 10-15 segundos. Luego dentengalo y diga: “Muy bien. Ese es todo el tiempo que tenemos para esa
palabra. Puedes bajar tu lápiz.”
• Si el alumno parece entender como escribir sobre la linea, no tiene que hacerle recordatorios despues
de la primera palabra, pero si no esta escribiendo sobre la línea repita: “Recuerda escribir sobre la
linea.”
STEM DOMAIN
Mathematics Subtest (Matemáticas)
Students who have a strong foundation in mathematics in early childhood have a better trajectory for math
achievement in their elementary school years. Informal and formal mathematics learning helps develop
students’ ability to problem solve and use math in academic and everyday settings. Thus, the Mathematics
subtest focuses on math skills related to numbers and counting, operations, patterning, and math in the real
world.

27
© 2023 The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston. All Rights Reserved.
TX-KEA User Guide
FEATURES OF THIS SUBTEST
The Mathematics subtest is divided into two parts. Teachers must complete both Math Part 1 and Math Part 2
to calculate the student’s score for the Math subtest:
• Math Part 1 includes teacher-recorded items
• Math Part 2 includes student-recorded items
• Untimed
• Teacher-recorded and student-selected responses
DIRECTIONS TEACHERRECORDED AND STUDENTSELECTED
Directions will be provided on the screen after the teacher enters the subtest.
1. Headphones are worn by the student.
2. Silently review the administration directions on the screen.
3. The student is told what to do through the headphones.
4. For Math Part 1 (teacher-recorded items), score the student’s verbal response by selecting an option
on the screen.
− Select which prompt(s) you used. See Allowable Prompts for more information.
5. For Math Part 2 (student-selected items), the student selects the best response and the computer
scores the response.
ALLOWABLE PROMPTS FOR MATHEMATICS SUBTEST
There may be rare occasions when a student provides a response that requires the teacher to follow up.
Allow 10 seconds for the student to respond before providing a prompt. The student can be prompted one
time. If the student does not reply with the correct answer within 10 seconds after the appropriate follow-up
statement is provided once, then the item is scored as incorrect.
• If the student does not begin counting for the counting aloud item, prompt the student by saying, “1,
2, 3.”
• If the student counts the items without stating the cardinal value say, “How many are there?”
SPECIAL SCORING INSTRUCTIONS FOR MATHEMATICS SUBTEST
The student’s final answer to the cardinal value is always the response that you will score. The student’s
counting of the objects is not taken into consideration for scoring.
Correct Responses:
• The student correctly counts the items and correctly says the cardinal value.

28
© 2023 The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston. All Rights Reserved.
TX-KEA User Guide
− Example: The student is shown 5 objects and counts aloud, “1, 2, 3, 4, 5.” The teacher will check
for cardinality by asking the student, “How many are there?” If the student says “5”, it is recorded
as a correct response.
• The student incorrectly counts the items and correctly says the cardinal value.
− Example: The student is shown 5 objects and counts aloud, “1, 2, 5, 6, 3.” The teacher will check
for cardinality by asking, “How many are there?” If the student says “5”, it is recorded as a correct
response since the student provided the correct cardinal value.
Incorrect Responses:
• The student provides no response or says, “I don’t know.”
• The student states any number, except the correct cardinal value.
• The student correctly counts the items and states an incorrect cardinal value.
− Example: The student is shown 5 objects and counts aloud, “1, 2, 3, 4, 5.” The teacher will check
for cardinality by asking, “How many are there?” If the student says “6” or any other number than
“5”, record this as an incorrect response.
Science & Engineering Subtest
(Ciencias)
The Science & Engineering subtest assesses knowledge of physical, life, earth, and space sciences, as well
as engineering applications of science. Teaching science and engineering capitalizes on students’ natural
curiosities about the world and supports predictive thinking, casual reasoning, and reflection on systems and
models. This subtest is available in English and Spanish.
FEATURES OF THIS SUBTEST
• Untimed
• Student-selected responses
DIRECTIONS
Directions will be provided on the screen after the teacher enters the subtest.
1. Headphones are worn by the student.
2. The student is told what to do through the headphones.
3. Pictures will appear on the screen as the computer provides the verbal prompt.
29
© 2023 The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston. All Rights Reserved.
TX-KEA User Guide
4. The student will select the picture that best answers the question.
5. The computer will score the student’s response.
ALLOWABLE PROMPTS FOR SCIENCE & ENGINEERING SUBTEST
Allow 10 seconds for the student to respond before providing the prompt. The student can be prompted one
time for each item. If the student does not reply with the correct answer within 10 seconds after prompting
once, then the item is scored as incorrect.
• If student does not respond after 10 seconds, say, “It’s okay to guess.”
SOCIAL EMOTIONAL SKILL DOMAIN
Social and Emotional Competence
Subtest (Socio-emocional)
The Social and Emotional Competence subtest focuses on students’ social and emotional skills within a
classroom setting. The subtest evaluates students’ pro-social skills, approaches to learning, and emotion
understanding.
FEATURES OF THIS SUBTEST
• Untimed
• Checklist
DIRECTIONS
Directions will be provided on the screen after the teacher enters the subtest.
1. Observe student interacting with other students and teachers.
2. Select a rating for each item based on student’s average observed behavior.
3. The computer will calculate the student’s score.
ALLOWABLE PROMPTS FOR SOCIAL & EMOTIONAL COMPETENCE SUBTEST
None.
30
© 2023 The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston. All Rights Reserved.
TX-KEA User Guide
SCORING SOCIAL AND EMOTIONAL COMPETENCE
Use the Social Emotional Scoring Guidelines, available on CLI Engage, to assist with scoring this subtest.
Input scores into the TX-KEA subtest on CLI Engage.
SPECIAL SCORING INSTRUCTIONS FOR SOCIAL & EMOTIONAL COMPETENCE
SUBTEST
Students are assessed using a checklist, which is completed by observing students interacting with others.
Teachers will record whether the student’s behavior occurs rarely, sometimes, or consistently.
We recommend that you complete the checklist after students have adjusted to kindergarten and you have
suciently observed students interacting with other students and teachers to best determine the student’s
social and emotional competence.
• “Rarely” means that the teacher may have observed the student displaying the behavior only a few
times.
• “Sometimes” means the teacher has observed the student’s behavior occurring from time to time
since the beginning of the school year (more than a few times, but not regularly).
• “Consistently” means that the teacher has observed the student frequently displaying the behavior.
EXAMPLES OF BEHAVIOR FOR SOCIAL & EMOTIONAL COMPETENCE SUBTEST
ITEMS
Appropriately asks for adult help when cannot
resolve peer conflict (without tattling)?
Pide ayuda de un adulto de manera adecuada
cuando no puede resolver conflictos con
compañeros (sin acusar)?
0
Rarely
Rara vez
1
Sometimes
Ocasionalmente
2
Consistently
Consistentemente
Feels and demonstrates pride for own
accomplishments?
Siente y demuestra orgullo por sus propios
logros?
0
Rarely
Rara vez
1
Sometimes
Ocasionalmente
2
Consistently
Consistentemente
Emotion Management Subtest
(Manejo de Emociones)
The Emotion Management subtest focuses on students’ ability to manage their emotions and respond
appropriately to an emotional experience. They are evaluated on whether they can adapt to the demands of a
classroom and school environment. This subtest is available in English and Spanish.

31
© 2023 The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston. All Rights Reserved.
TX-KEA User Guide
FEATURES OF THIS SUBTEST
• Untimed
• Checklist
DIRECTIONS
Directions will be provided on the screen after the teacher enters the subtest.
1. Observe student interacting with other students and teachers.
2. Select a rating for each item based on student’s average observed behavior.
3. The computer will calculate the student’s score.
ALLOWABLE PROMPTS FOR EMOTION MANAGEMENT SUBTEST
None.
SPECIAL SCORING INSTRUCTIONS FOR EMOTION MANAGEMENT SUBTEST
Students are assessed using a checklist, which is completed by observing students interacting with others.
Teachers will record whether the student’s behavior occurs rarely, sometimes, or consistently.
We recommend that you complete the checklist after students have adjusted to kindergarten and you have
suciently observed students interacting with other students and teachers to best determine the student’s
emotion management.
• “Rarely” means that the teacher may have observed the student displaying the behavior a few times.
• “Sometimes” means the teacher has observed the student’s behavior occurring sometimes since the
beginning of the school year.
• “Consistently” means that the teacher has observed the student frequently displaying the behavior.
EXECUTIVE FUNCTIONING DOMAIN
The Executive Functioning domain addresses the cognitive skills used by students to plan, problem solve, and
follow classroom rules. We focus on three executive functioning skills – Inhibition, Working Memory, and
Attention. These skills help students manage their own learning and behavior in the classroom.

32
© 2023 The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston. All Rights Reserved.
TX-KEA User Guide
Working Memory Subtest (Memoria)
Students are assessed on their ability to hold in memory 1 – 3 pieces of information in an increasingly
complex setting. In this subtest, students recall where cars are parked in a garage. The number of cars and the
number of parking spaces increases as the student progresses. This subtest is available in English and Spanish.
FEATURES OF THIS SUBTEST
• Untimed
• Student-selected responses
DIRECTIONS
Directions will be provided on the screen after the teacher enters the subtest.
1. Headphones are worn by the student.
2. The student is told what to do through the headphones.
3. Pictures will appear on the screen as the computer provides the verbal prompt.
4. Students will recall and select the spot where a car was previously parked.
5. The computer will score the student’s response.
ALLOWABLE PROMPTS FOR WORKING MEMORY SUBTEST
Allow 10 seconds for the student to respond before providing a prompt. The student can be prompted one
time. If the student does not reply with the correct answer within 10 seconds after the appropriate follow-up
statement is provided once, then the item is scored as incorrect.
• If student does not respond after 10 seconds, you can prompt student by saying, “It’s okay to guess.”
Inhibition Subtest (Inhibición)
Students are asked to respond accurately to a specific stimulus (e.g., butterfly), and withhold, or inhibit, a
response to a dierent stimulus (e.g., bee). This task involves students catching butterflies in a butterfly net
but NOT catching bees for a certain time limit. They are warned that the butterflies are fast and that the
students must be fast too. Scores reflect the student’s ability to respond accurately while inhibiting a response.
This subtest is available in English and Spanish.

33
© 2023 The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston. All Rights Reserved.
TX-KEA User Guide
FEATURES OF THIS SUBTEST
• Timed
• Student-selected responses
DIRECTIONS
Directions will be provided on the screen after the teacher enters the subtest.
1. Headphones are worn by the student.
2. The student is told what to do through the headphones.
3. Pictures will appear on the screen as the computer provides the verbal prompt.
4. The student will attempt to only “catch” butterflies by touching the screen or clicking the mouse over
the image when a butterfly appears on screen.
5. The computer will score the student’s response.
ALLOWABLE PROMPTS FOR INHIBITION SUBTEST
Allow 10 seconds for the student to respond before providing a prompt. The student can be prompted one
time. If the student does not reply with the correct answer within 10 seconds after the appropriate follow-up
statement is provided once, then the item is scored as incorrect.
• If student does not respond after 10 seconds, you can prompt student by saying, “It’s okay to guess.”
Attention Subtest (Atención)
Students are assessed on their ability to focus their attention, stay on task, as well as quickly and accurately
focus on relevant features of the task. They are provided 2 minutes to make as many correct matches as
possible between the target object, a flower, and 5 answer choices, other flowers. This subtest is available in
English and Spanish.
FEATURES OF THIS SUBTEST
• Timed
• Student-selected responses
34
© 2023 The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston. All Rights Reserved.
TX-KEA User Guide
DIRECTIONS
Directions will be provided on the screen after the teacher enters the subtest.
1. Headphones are worn by the student.
2. The student is told what to do through the headphones.
3. Pictures will appear on the screen as the computer provides the verbal prompt.
4. The student will attempt to match the flower in the top row to a flower in the bottom row from five
response choices by touching the screen or clicking the mouse over a flower in the bottom row.
5. The computer will score the student’s response.
ALLOWABLE PROMPTS FOR ATTENTION SUBTEST
Allow 10 seconds for the student to respond before providing a prompt. The student can be prompted one
time. If the student does not reply with the correct answer within 10 seconds after the appropriate follow-up
statement is provided once, then the item is scored as incorrect.
• If student does not respond after 10 seconds, you can prompt student by saying, “It’s okay to guess.”
ACADEMIC MOTOR SKILLS DOMAIN
Academic Motor Skills Subtest
(Motricidad Académica)
The Academic Motor subtest includes items that evaluate many of the motor skills required for successful
completion of school activities. It is important to understand the motor skills of students because they form
the basis for the way young students learn. In fact, motor skills underlie aspects of cognitive development and
social development. This subtest is available in English and Spanish.
FEATURES OF THIS SUBTEST
• Untimed
• Checklist

35
© 2023 The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston. All Rights Reserved.
TX-KEA User Guide
DIRECTIONS
Directions will be provided on the screen after the teacher enters the subtest.
1. Observe student’s motor behaviors in the classroom and on the playground.
2. Select a rating for each item based on student’s average observed behavior.
3. The computer will calculate the student’s score.
SCORING ACADEMIC MOTOR SKILLS
Use the Academic Motor Skills Scoring Guidelines on CLI Engage to assist with scoring this subtest. Input
scores into the TX-KEA subtest on CLI Engage.
SPECIAL SCORING INSTRUCTIONS FOR ACADEMIC MOTOR SUBTEST
Students are assessed using a checklist, which is completed by observing motor behaviors. Teachers will
record whether the student’s behavior is typical for their age, delayed, or if the teacher has not observed the
behavior. While it is recognized that questionnaire data introduces some ambiguity (i.e., ensuring that teacher
ratings are consistent across students, schools, and school districts), these types of scales can be an ecient
means to collect data on large groups of students.
We recommend that you complete the checklist after students have adjusted to kindergarten and you have
suciently observed students motor behaviors.
“Not Observed” means that the teacher has not yet observed the student displaying the behavior.
• Given that TX-KEA was designed to be used by kindergarten teachers approximately 1 month after
school entry, we do not anticipate the need for teachers to use the “Not Observed” anchor routinely.
For instance, by the time TX-KEA is administered, we anticipate that teachers would be able to spend
time with all students in their classroom participating in small group activities to observe multiple
items (e.g., use of a 3-fingered pencil grip, name writing, ability to draw recognizable shapes). At the
minimum, a child’s ability to appropriately use writing implements can be observed as the students
complete the Spelling subtest. In addition, teachers can easily ask students to complete many of these
activities (e.g., ability to use scissors, sorting activities, ability to trace letters, etc.) if these skills have
not observed within a natural setting.
“Delayed” means the student’s motor skill is behind the development of their peers.
• The “Delayed” anchor should be used when the student’s skills are clearly outside of the norm. The
“Delayed” rating should be utilized in cases where the student is clearly outside of the norm for
kindergarten (e.g., bottom 10 percent of students in kindergarten). In terms of using a 3-fingered
pencil grip, a student who receives a “Delayed” score would be one who is unable to maintain the
tripod grip even after being provided with assistance. In terms of drawing recognizable shapes, a
student who receives a “Delayed” score would have diculty drawing any recognizable shapes.
“Typical for Age” means that the student’s motor skill is developmentally appropriate.
• The “Typical for Age” rating anchor should be used for students who are able to complete activities
suggested in the Academic Motor Skills category in a manner that is similar to most kindergarten
36
© 2023 The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston. All Rights Reserved.
TX-KEA User Guide
aged students. In relation to examples included in questionnaire, students do NOT have to be able to
complete all of the examples. For example, a student’s ability to draw recognizable shapes is evaluated
in one of the items. Examples included in this item include the ability to draw a circle, square, smiley
face, or stick figure. In order to receive an item score of “Typical for Age”, the student should be able
to successfully draw some but not all of the suggested shapes/figures.
Language of Administration
The Spanish and English versions of TX-KEA have been evaluated to ensure its reliability and validity with
Spanish speaking and English learner populations.
SELECTING THE LANGUAGE OF ADMINISTRATION
The decision to assess Spanish-speaking English learners in Spanish, or in both English and Spanish, should
follow the recommendations of the campus Language Proficiency Assessment Committee (LPAC). Decisions
on the language of assessment for native English speakers who are participating in Spanish-English dual-
language immersion programs is left to the discretion of program personnel.
MEASURING LANGUAGE PROFICIENCY
TX-KEA has not been validated for use as a measure of language proficiency in either language.
USING THE SPANISH OR ENGLISH TXKEA TO GUIDE INSTRUCTION
When using TX-KEA results to guide instruction, you should assess students in the language of instruction to
determine current levels and goals. You may choose to also assess in the alternate language if you can make
use of the student’s skills in that language.
ASSESSING IN BOTH LANGUAGES
TX-KEA allows you the flexibility to assess students in one or both languages. Students can be assessed in both
English and Spanish for individual subtests.
To help guide instructional planning, a teacher may wish to learn more about a student’s performance in
Spanish even if the student is receiving all English instruction. For example:
• It may be useful to know if a student has well developed phonological awareness skills in Spanish
relative to their age. This information may indicate that the student has skills in place for developing
phonological awareness in English.
• Alternatively, it may be useful to know if a student has limited phonological awareness skills in
Spanish as this may indicate the need for further instruction in English and/or Spanish to support
optimal phonological awareness growth. By assessing the student in both languages, the teacher can
better plan instruction to extend strengths and support weaknesses.
37
© 2023 The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston. All Rights Reserved.
TX-KEA User Guide
ASSESSING IN THE MOST PROFICIENT LANGUAGE
There may be instances when you find it helpful to administer specific subtests in a student’s most proficient
language.
• Example 1: Student A is a native Spanish speaker. Their performance on the language subtests in
English is very low. The teacher may find it helpful to administer the same subtest in Spanish to
gather some additional information about their strengths and needs.
• Example 2: Student B is also a native Spanish speaker. Their performance on the self-regulation
subtest administered in English is very low. The teacher may choose to assess self-regulation in
Spanish to be sure low English proficiency is not being confused with poor self-regulation.
LINGUISTIC ACCOMMODATIONS
Linguistic accommodations are those that reduce the English proficiency demands of the test without altering
the construct the test is intended to measure.
• Time accommodations are built into TX-KEA since the language, literacy, and cognitive subtests of
TX-KEA are not timed.
• An oral translation of the English TX-KEA test instructions can be provided to English learners who
do not speak Spanish. The person providing the translation should be a fluent speaker of the student’s
language.
• Translation of test items and use of dictionaries are not appropriate linguistic accommodations for
TX-KEA.
Assessing Students with Disabilities
Multiple sources were used to determine the best recommendations to accommodate TX-KEA for use with
students with disabilities. This included a review of the Texas Education Agency’s published accommodations
recommendations and federal sources that provide considerations and accommodations for students with
disabilities. Feedback was collected from special educators, diagnosticians, and other district professionals,
such as speech, occupational, and physical therapists. Based on feedback from these professionals, attempts
were made to build an assessment system that could be used with a broad range of students with varying
disabilities.
When making a determination about whether or not TX-KEA is appropriate for a student with a disability,
consider the following factors:
• TX-KEA was NOT designed and should NOT be used to identify a student as having a disability.
• TX-KEA was not normed for students with disabilities. This means that we do not have normative
information about how students with a particular disability would perform on these measures that
could be used for comparison when evaluating the performance of a child with a disability.
SHOULD I USE TXKEA WITH A STUDENT WITH A DISABILITY?
• Students with disabilities have a wide range of skills and many students with mild forms of

38
© 2023 The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston. All Rights Reserved.
TX-KEA User Guide
disabilities, such as a language delay, can easily complete many of the TX-KEA subtests with no, or
minimal, accommodations.
• Understanding how a student with a disability scores in relation to typically developing peers can
provide teachers with information that they can share with parents about the relative strengths and
weaknesses of students with disabilities. For example, you may have a student with a language delay
that scores within normal limits on the Math and Self-Regulation subtests, but struggle on subtests
evaluating phonological awareness skills. This provides a wide range of information about this
student’s strengths and where growth is needed.
TEXAS EDUCATION AGENCY TEA ACCOMMODATIONS TO CONSIDER
The TEA provides detailed information about the provision of accommodations when completing state
assessments on their website. Even though TX-KEA is not a mandated state assessment, guidelines provided
by TEA should be used as a guide to determine the types of accommodations that can be made to TX-KEA.
Please see the Accommodations Resources section on the TEA website.
ACCOMMODATIONS WITH TXKEA
TX-KEA provides two classes of recommendations within the TEA model. 1) Low Risk and 2) High Risk.
1. Low Risk Decision Rule: Accommodations that DO NOT alter or change the wording, scoring
criteria, or time limits imposed on certain TX-KEA subtests are considered low risk and easily
approved and implemented by ARD or 504 committee. Many TEA accommodations are appropriate
for TX-KEA subtests with low risk to the integrity of the assessment. Examples of Low Risk
accommodations are provided below.
− Example 1: Use of individualized structured reminders to help a student pay attention, or get
ready for the next item. This would be seen as conforming to acceptable test practices for all
students.
− Example 2: Use of amplification and projection devices with a range of students with visual or
hearing deficits.
− Example 3: Manipulation of test materials is considered low risk. Student-selected response
items can be answered by assistive technology products, such as alternative keyboards, electronic
pointing devices, sip-and-pu systems, wands and sticks, joysticks, trackballs, and other tools.
− Other Low Risk Accommodations: Oral/signed presentation of test items would also be
acceptable. Math manipulatives are included in some of the easier TX-KEA counting and
operation items and would be acceptable accommodations.
2. High Risk Decision Rule: Accommodations that DO alter or change the wording, scoring criteria, or
time limits imposed on certain TX-KEA subtests are considered high risk. High Risk accommodations
may impact the validity and integrity of the assessment making interpretation more challenging. High
risk accommodations may be helpful when using TX-KEA to evaluate a student’s relative strengths
and weaknesses rather than using the scores to relate performance to the norm group. These would
not be norm-based, but may provide meaningful information for teachers and professionals for
children’s learning and educational planning.
39
© 2023 The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston. All Rights Reserved.
TX-KEA User Guide
− Example 1: Providing extra time or an extra day for timed tests. If violated, the test isn’t valid for
its purpose.
− Example 2: Manipulating or substituting words for vocabulary and comprehension tests.
Accommodations that substantively change test items in any way should be avoided.
− Example 3: Changing scoring criteria to accommodate student’s response style. For example,
when counting on the Math screener, the item is scored based upon the cardinal value that is
provided by the child. Changing the scoring criteria to give credit for students who are able to
count objects correctly but do not understand the concept of cardinal value would be considered
to be high risk and should be avoided.
OTHER RECOMMENDATIONS & CONSIDERATIONS
While not technically an accommodation, it is hoped that good testing practices are utilized when teachers
use TX-KEA in a classroom. Establishment of rapport with young students is critical for TX-KEA assessments.
Students should not be penalized for words that are poorly articulated. Kindergarteners often struggle
articulating words clearly. A good rule of thumb is that if two adults could easily determine what word the
student said then the verbal response should be scored.
Teacher and administrators should make reasonable eorts to provide appropriate accommodations that
will allow students with disabilities the opportunity to demonstrate their knowledge. The best judges of the
appropriateness of the accommodations are the professional sta who has the most contact with the student
with a disability. Creative accommodation approaches that allow students with disabilities to successfully
complete TX-KEA subtests but do not violate the content of the assessment would be welcomed by the
authors of TX-KEA. TEA Guidelines should be considered when attempting to determine appropriate
accommodations.
40
© 2023 The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston. All Rights Reserved.
TX-KEA User Guide
FAQs
Question Answer
How were TX-KEA items developed? Content was developed to align with Texas
Prekindergarten Guidelines and kindergarten
Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS).
A range of items, from easy to hard, are
represented. It is not expected that all students
will answer all items correctly. The purpose is to
learn about the instructional needs and abilities
of students.
Can I compare end-of-year CIRCLE Progress
Monitoring data to TX-KEA data?
CIRCLE Progress Monitoring and TX-KEA are
conceptually aligned. However, they are not
vertically or horizontally equated, so their scores
are not comparable at this time.
Can you provide background on the
selection of Spanish words, prompts, letter
pronunciations etc.?
The selection of prompts, words, and general
item content used in the Spanish TX-KEA
was guided by criteria related to the construct
assessed in each subtest. In general, selection
was guided by curricular relevance, linguistic,
and conceptual features targeted by an item
and other developmental criteria such as age
of acquisition and age of instruction. All items
in Spanish were reviewed by committees of
Spanish speakers representing various dialects
of Spanish. Item translations were also done in
committee and when appropriate underwent
back translation procedures to ensure adherence
to the construct being measured.
Can the kindergarten entry assessment be
used at the end of prekindergarten?
The kindergarten entry assessment is intended
to be administered between early September
and the end of October of the kindergarten
school year. Assessment items are specifically
designed for children at that age, so giving it
several months early may invalidate the results.
Is TX-KEA computer adaptive? TX-KEA is not an adaptive assessment.
